Assessment of exposures outside - Normal operation
For endpoints corresponding of the type Dose and Outside, SAFRAN provides support for assessing doses from exposures outside the facilities. Which dose assessment method is applied will depend on the type of impact that has the scenario linked to the assessment endpoint of interest. The different situations that may arise are considered below.
Releases to air
For endpoints of the type “outside” which are linked to scenarios with impacts of the type “releases to air”, SAFRAN will apply the procedure shown in Table 4.7 for assessment of doses outside the facilities. The DCF for releases to air during normal operation are defined as the effective annual dose to a member of the public resulting from an unit constant release rate of a radionuclide during the whole period when the releases take place. The SAFRAN Internal Database includes values of the Dose Conversion Factors (DCF). These have been calculated with the SAFCALC Module for routine atmospheric releases outside. The user can add own values of the DCFs obtained for specific situations using SAFCALC or any other tool.
Table 4.7. Doses outside the facility from releases to air outside the facility during normal operation
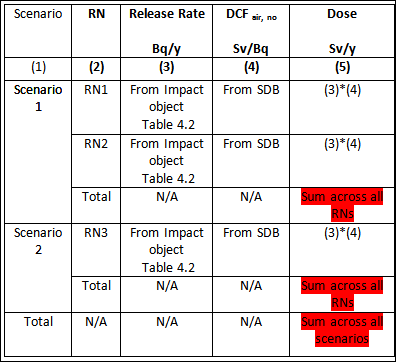
RN – radionuclide, SDB – SAFRAN Internal Database, N/A – not applicable.For Table 4.2 - see sections Releases to air. The cell marked in read is used in the Analysis Module for comparison of hazards.
Definition of columns in Table 4.7:
-
Column 1. Short name of the scenario.
-
Column 2. Short name of the radionuclide (RN).
-
Column 3. Radionuclide release rate outside the facility.
-
Column 4. Dose Conversion Factor for releases to air during normal operation.
-
Column 5. Annual dose from the releases outside.
Columns in Table 4.7 that can be modified by the user: 3 - to define the release rate outside the facility, column 4 – for entering the dose conversion factor, column 5 – for entering directly the dose values.
Liquid discharges
For endpoints of the type “outside” which are linked to scenarios with impacts of the type “liquid discharges”, SAFRAN will apply the procedure shown in Table 4.8 for assessment of doses outside the facilities. The DCF for liquid discharges during normal operation are defined as the effective annual dose to a member of the public resulting from an unit constant discharge rate of a radionuclide during the whole period when the releases take place. The SAFRAN Internal Database includes values of the Dose Conversion Factors (DCF). These have been calculated with the SAFCALC Module for routine liquid discharges. The user can add own values of the DCFs obtained for specific situations using SAFCALC or any other tool.
Table 4.8. Doses outside the facility from liquid discharges outside the facility during normal operation
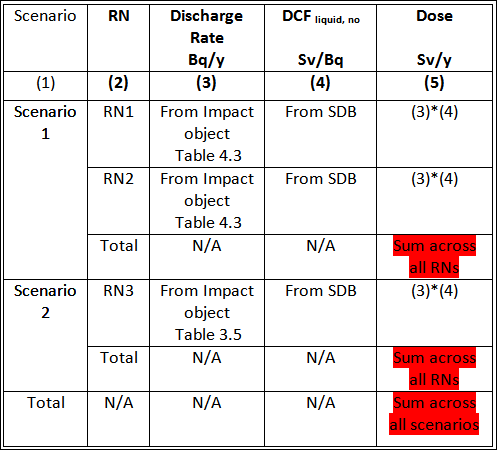
RN – radionuclide, SDB – SAFRAN Internal Database, N/A – not applicable. For Table 4.3 - see section Liquid discharges.The cell marked in read is used in the Analysis Module for comparison of hazards.
Definition of columns in Table 4.8:
- Column 1. Short name of the scenario.
- Column 2. Short name of the radionuclide (RN).
- Column 3. Radionuclide discharge rate outside the facility.
- Column 4. Dose Conversion Factor for liquid discharges during normal operation.
- Column 5. Annual dose from the liquid discharges outside.
Columns in Table 4.8 that can be modified by the user: 3 - to define the discharge rate outside the facility, column 4 – for entering the dose conversion factor, column 5 – for entering directly the dose values.